Understanding Reproductive Health: A Comprehensive Guide for Men and Women
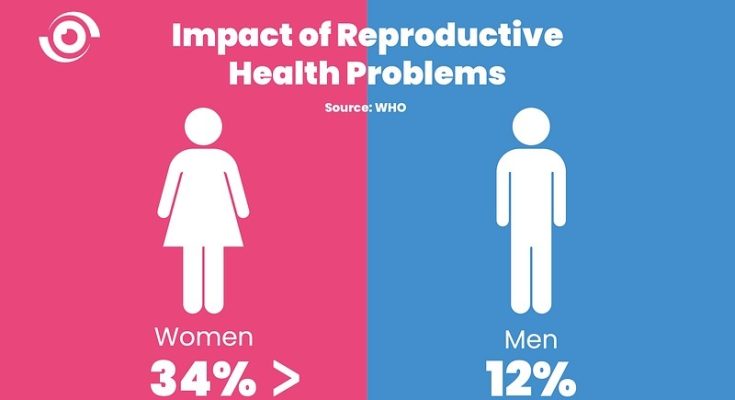
Reproductive health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, yet conversations often focus disproportionately on women’s health. This oversight is problematic, as many serious conditions impact both genders. Early recognition of symptoms significantly improves treatment outcomes, preventing long-term health complications and even reducing cancer risks. This blog post delves into common reproductive health conditions affecting both men and women, providing insights from leading health organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and Mayo Clinic, alongside actionable prevention strategies and treatment options.
The Importance of Reproductive Health Awareness
A Complex System Requiring Attention
Our reproductive system, a sophisticated network of organs and hormones, plays vital roles in sexual health, fertility, and hormone regulation. Disruptions to this system can manifest as pain, infections, infertility, or more severe problems including chronic illnesses and cancer. Sadly, many individuals are unaware of early warning signs, often delaying medical attention due to embarrassment or stigma. This underscores the urgent need for improved education and early detection initiatives.

Common and Dangerous Reproductive Conditions Affecting Both Sexes
Several conditions significantly impact both men and women’s reproductive health. Understanding these conditions and their potential consequences is paramount for proactive healthcare.
1. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Primarily affecting women, PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs, frequently stemming from untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia or gonorrhea. Left untreated, PID can cause irreversible damage to the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, escalating the risk of infertility and ectopic pregnancy. While men might not exhibit symptoms, they can unknowingly transmit the causative infections. Regular STI testing and safe sexual practices are therefore crucial for both genders.
2. Human Papillomavirus (HPV)

HPV, one of the most prevalent STIs globally, affects both men and women. Although many cases resolve spontaneously, certain HPV strains can lead to cervical cancer in women, penile cancer in men, and throat or anal cancer in both. The HPV vaccine offers highly effective protection against the cancer-causing strains. The CDC recommends vaccination for both boys and girls, ideally before sexual initiation.
3. Genital Herpes
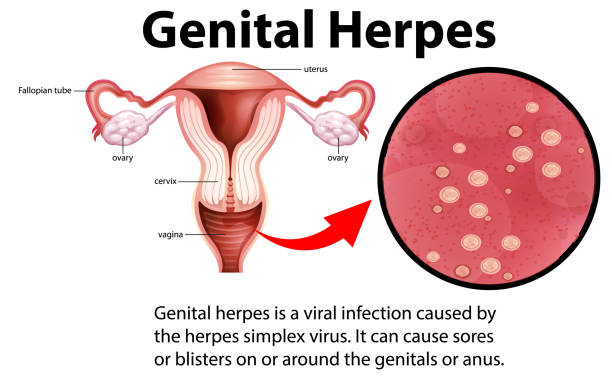
Caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), genital herpes is a chronic condition characterized by recurrent outbreaks. While not usually life-threatening, it causes painful sores, emotional distress, and potential pregnancy complications. Importantly, many individuals with HSV remain asymptomatic, highlighting the importance of safe sex practices and open communication with partners.
4. Gender-Specific Conditions with Overlapping Symptoms
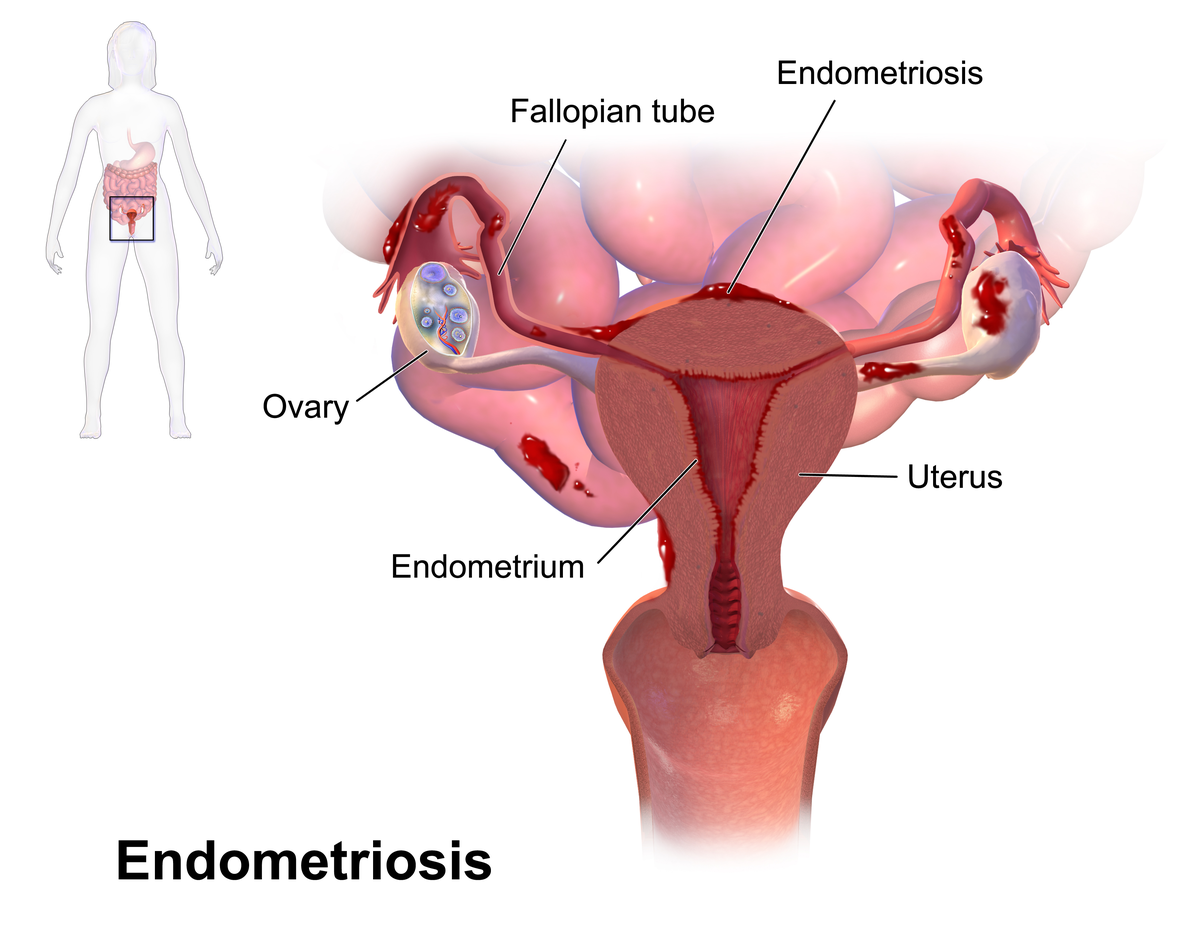
While some conditions are gender-specific, they can share similar symptoms, complicating diagnosis. Endometriosis, in women, involves the growth of uterine-like tissue outside the uterus, causing inflammation, pain, and fertility issues. In men, chronic prostatitis, inflammation of the prostate gland, frequently presents with pelvic pain and urinary problems. Both conditions can impact sexual health and quality of life. Early diagnosis and management, often involving lifestyle modifications, pain management, physical therapy, or hormonal treatments, are critical.
5. Infertility: A Shared Challenge
Infertility, affecting roughly one in six couples globally according to the WHO, is a condition impacting both men and women equally. Contributing factors include hormonal imbalances, structural abnormalities, lifestyle factors (such as smoking or poor diet), and untreated infections. Comprehensive fertility testing for both partners is essential, with treatments ranging from medication to advanced techniques like IVF.
Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
Early detection is key to successful treatment. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following:

- Persistent pelvic or lower abdominal pain
- Unusual vaginal discharge or odor
- Painful urination or intercourse
- Irregular menstrual cycles (women)
- Erectile dysfunction or testicular pain (men)
- Chronic fatigue and low libido
- Fever with pelvic discomfort
Preventive Measures for Optimal Reproductive Health
Proactive steps significantly reduce the risk of reproductive health problems. These include:
- Safe Sexual Practices: Consistent use of barrier protection (condoms) and regular STI testing if sexually active with multiple partners.
- Vaccination: The HPV vaccine is a crucial preventative measure.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of smoking and excessive alcohol.
- Stress Management: Implementing stress-reduction techniques to maintain hormonal balance.
- Regular Checkups: Annual physicals and gynecological or urological exams are essential.
- Open Communication: Honest conversations with partners about sexual health foster trust and understanding.
Treatment and Support
Treatment options vary based on the specific condition, encompassing antibiotics for infections, hormonal therapies for conditions like endometriosis or PCOS, counseling for emotional support, and surgical interventions when necessary. Support groups offer valuable assistance for those managing chronic conditions or infertility. Numerous healthcare facilities provide comprehensive reproductive health services regardless of gender. Seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
Conclusion: Shared Responsibility for Reproductive Health
Reproductive health is not solely a women’s issue—it affects everyone. Conditions like HPV, STIs, infertility, and chronic pelvic disorders underscore the shared responsibility in prevention, early detection, and care. Most reproductive health problems are manageable and often preventable through education, open communication, and routine healthcare. Don’t wait for symptoms to worsen—take proactive steps today to safeguard your reproductive health.